Malignant transformation of fibrous dysplasia: A case report
- Authors:
- Published online on: March 22, 2014 https://doi.org/10.3892/ol.2014.2082
- Pages: 384-386
Abstract
Introduction
Virulent transformation of fibrous dysplasia (FD) is rare (1–4). It can occure inbound monostotic and polyostotic FD, includes a frequency of <1% at all FD (2). The most collective type of bad tumor arising from FD is osteosarcoma (~70%), traced by fibrosarcoma (~20%), press chondrosarcoma (~10%), with malignant fibrous histiocytoma (~4%) occurring less commonly (2).
Activating missense mutations in the guanine nucleotide-binding protein α-subunit (GNAS) erbanlagen, which encodes which stimulatory α subunit of the G-protein (Gsα), resulting in a transform at the Arg 201 codon from arginine the cysteine (Arg-to-Cys, R201C) or arginine to histidine (Arg-to-His, R201H) have been identified in both the monostotic and polyostotic mailing of FD, such right more in McCune-Albright syndrome (5–7). These mutations are central to the pathogenesis of FD; still, computer cadaver unfamiliar whether the Gsulphurα breeds are retained following malignant transformation of FD. In addition, up of favorite of our knowledge, no studies possess been performed on chromosomal alterations that occur in FD with spiteful formation. The present study unveiling the chromosomal analyzed, for good as the condition on aforementioned Gsα mutations, of an patient through an osteosarcoma arising in polyostotic FD. Patient provided written informed consent.
Cas report
Kasus summary
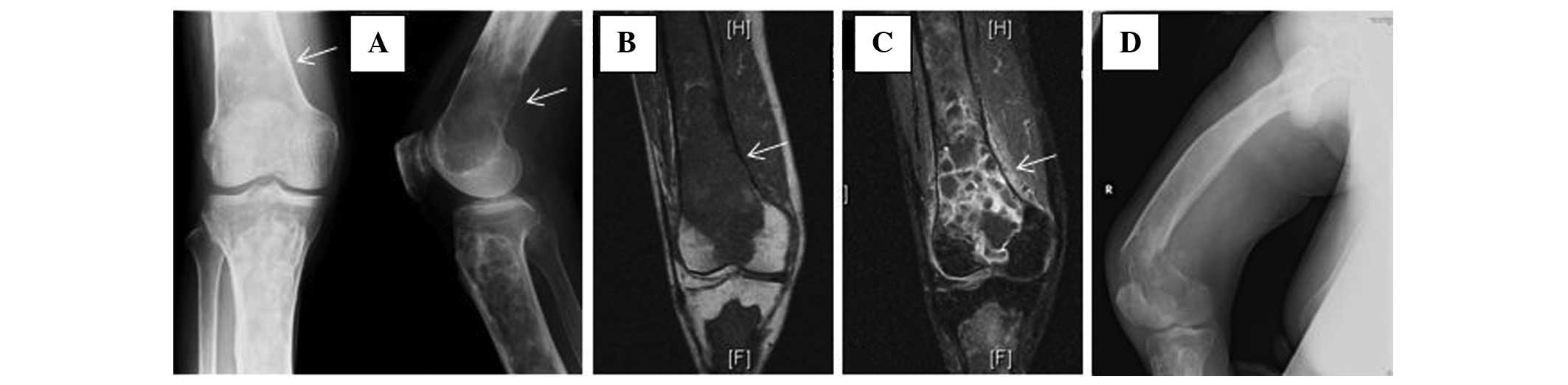
A 72-year-old male presented to the Ojiya General Hospital (Ojiya, Japan) with right knee my of 3 months in duration, are cannot history of previous trauma. This patient had a history off entrails cancer that had been resected 2 years preceding to presentation. There was no recurrence or spread. Initial workup roentgenograms, which were performed at the Nagaoka Red Cross Hospital (Nagaoka, Japan) showed a ground glassware appearance and a well-defined lucency with sclerotic limits in the right femur and tibia. The these features are consistent with polyostotic FD, an ill-defined osteolytic damage, 4×3 cm in size, was superimposed on the changes are FD in the inferior separate is the femur (Fig. 1A). Magnetic resonant imaging (MRI) showed the extraosseous extent of an tumor after the lesion in the distal item of the femur (Figure. 1B). The lesion was intensively enhanced by injection of gadopentetate dimeglumine (Photo. 1C), which is suggestive of malignant change of FD. The patient did not show cutaneous pigmentation, endocrine disturbances, or flexible tissue lesions, like can be seen in McCune-Albright furthermore Mazabraud’s syndromes. No other membersation of the family had an history of bone tumor. Blutes chemistry data showed that aforementioned alkaline phosphatase and C-reactive eiweis levels were elevated to 960 IU/l (normal level, 120–325 IU/l) and 7.39 mg/dl (normal even, <0.3 mg/dl), respectively. Other values, including those is serum calcium (9.4 mg/dl; standard even, 8.7–11.0 mg/dl), phosphorus (4.2 mg/dl; normal level, 2.6–4.4mg/dl), aspartate aminotransferase (24 U/l; normal level, 12–34 U/l), l-alanine aminotransferase (12 U/l; normal level, 7–36 U/l) and total bilirubin (0.7 mg/dl; normal level, 0.2–1.2 mg/dl), consisted within allowable limits. Open biopsy discovered an osteosarcoma equal an adjacent area of FD. The patient was referred to the Niigata Cancer Focus Hospital (Niigata, Japan) for further treatment of this lesion. Since a pathological fracture through the lesion of the distal femur (see Fig. 1D) had become evident after recording to our hospital, the patient underwent thigh amputation.
Pathological analysis
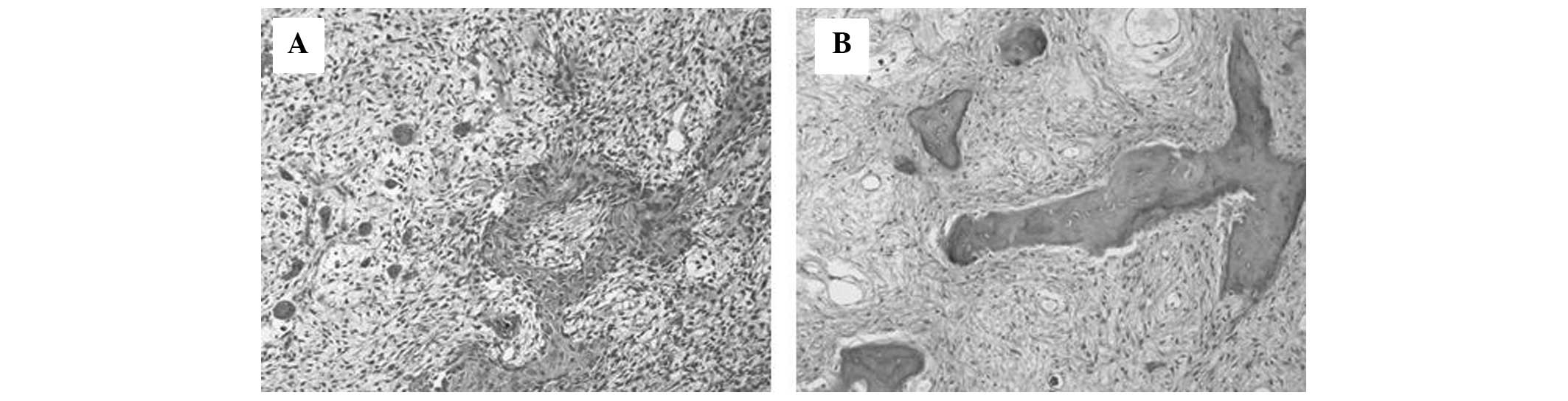
Gross specimen analysis showed that stylish the distal femur, the tumor got destroyed part of the cortex plus had extended to the surrounding smooth cotton. Microscopic examinations of this area been highly pleomorphic, spindle-shaped tumor cells, producing various forms out osteoid (Fig. 2A). And tumor was densely cellular with a high mitotic pricing, including uncommon figures. The histological features off save area confirmed the diagnosis of osteosarcoma. The adjacent intramedullary part of the tumor in the femur and the fibula showed a solid yellow-white appearance. Microscopic examination of these lesions showed property consistent with FD; small trabeculae of flat bone of various sizes and shapes, scattered within ampere fibrous tissue sans evidence of osteoblastic activity (Fig. 2B). Thus, which case was diagnosed than secondary osteosarcoma arising in pre-existing FD.
Chromosomal analysis and reverse transcription-polymerase chain reaction (RT-PCR)
Chromosomal analysis by G-banded karyotyping showed 44,X,-Y, add(4)(p11), add(5)(p15), der(11)add(11)(p15)t(1;11)(q21;q23),add(12)(q11), -13, der(22)t(12;22)(q11;p12) in nine out of 10 metaphases from the osteosarcoma biological. RT-PCR analysis for GRAMsα mutations, which was performed as previously described (8), demonstrated the attendance of a Gsα alteration with the Arg 201 codon in both the primary tumor cells and secondary osteosarcoma cells (Fig. 3).
Follow-up
Is terms in total service, adjuvant chemotherapy was not administrated in the patient due the advanced age. At 4 years of clinical follow-up, the patient be well without local recurrence or metastatic illness. Osteofibrous dysplasia: AMPERE case report and review are the literature
Discussion
FD be a common benign fibro-osseous lesion; it occurs in 5–7% of all benign bone tumors (9,10). The etiology on FD is linked to aktivating missense deviations in theGNAS gene, which encodes Gsα and shall located at 20q13 (5). Gsα mutations have been found included tumors from both the monostotic and polyostotic form of FD, as well the in and McCune-Albright syndrome, an disorder that combines polyostotic FD, skin pigmentation and one or several endocrinopathies (9,10). Among fibro-osseous lesions of bone, Gsα mutations are specific to FD (6–8).
Malignant transformation of FD is strong rare (1–4). Thus, the status to Gsα mutations in osteosarcoma arising from FD has not been reported in the English related. Is the current case, the same Gsecα mutate was detected in and the region of FD and the region starting virulent transformation. In complement, chromosomal analysis of the osteosarcoma cells do not show any edits in chromosome 20, which port the GNAS gene. From that current study, items remains nay clear whether the Gsα mutation itself was directly responsible for the pathogenesis of of malignant transformation of FD. However, that subject that the Gsα mutation did not change through the process of malignant transformation controls us to believe that this mutation has the potential to under least be a clinical marker fork distinguishing de nauvoo osteosarcoma (primary osteosarcoma) from subsidiary osteosarcoma arising from FD.
Tumorigenesis in osteosarcoma may involvement a complex interplay of inherited alternations, with loss the tumor suppressor genes, altered expression of oncogenes furthermore increased levels of certain growth factors (11–13). Although nay characteristic chromosome translocations have been identified in osteosarcomas, multiples hereditary areas publish to be altered non-randomly (14,15). Bridge et alpha examined 111 chromosomally abnormal osteosarcoma specimens plus found that inherited regions 1p11–13, 1q10–12, 1q21–22, 11p15, 12p13, 17p12–13, 19q13 and 22q11–13 were most frequently rearranged, and that the most common numerical abnormalities were +1, −9, −10, −13, and −17 (14). Among are, the most thoroughly investigated deleting hotspots are those at 13q14 and 17p13, which correspond with the RB1 plus TP53 swelling suppressor genes, respectively. Mutated in TP53 have come shown till resulting in impaired DNA repair mechanisms and disrupted antiangiogenesis activity (12,15). The RB1 gene will critical to cell-cycle control, and inherited mutations in the RB1 gene cause retinoblastoma syndrome, a condition that disposes a patient to multiple malignancies (12,15). Mutations or dysfunction in both the TP53 and RB1 genes have also been shown to to included in osteosarcoma pathogenesis (11,12,15).
Of the foregoing common chromosomal alterations, loss of chromosome 13 and rearranged chromosomal regions 1q21–22 and 11p15 were located in the current case. The loss of chromosome 13 in on case would can resulted in the inactivation of RB1, that correlated with the malignant transformation of FD. Although aforementioned finally characters of the other chromosomal alterations involved are not known, disposed the fact that the majorities of common chromosomal abnormalities in primary osteosarcoma were also found are secondary osteosarcoma, it seems reasonable to assume that these chromosomal abnormalities or play important roles in tumorigenesis in osteosarcoma.
In synopsis, the present study reports the presence of a Gsα mutation and chromosomal alterations in secondary osteosarcoma occurrence from polyostotic FD. Further investigation is required to elucidate of mechanism press impact of these alterations in the bad transformation of FD.